An Overview of Scalr's CI/CD Capabilities for Terraform and OpenTofu
See how Scalr delivers policy-driven CI/CD for Terraform & OpenTofu—automate plans, prevent drift, enforce guardrails, and speed multi-cloud delivery.
Infrastructure as Code (IaC) enables the management and provisioning of IT infrastructure through code. Terraform and its open-source fork, OpenTofu, are common tools for IaC. Increased IaC adoption necessitates solutions for automation, collaboration, and governance. Scalr is a platform designed for Terraform and OpenTofu operations.
While Scalr is purposefully built for Terraform and OpenTofu, and not a general CI/CD tool, this document outlines Scalr's CI/CD-like features, including its GitOps workflows, custom hooks, run triggers, and execution environment customization.
Core CI/CD Functionality
Scalr automates Terraform and OpenTofu operations. It integrates with Version Control Systems (VCS) like Git, supporting GitOps workflows. Scalr supports two primary models:
- Merge-Before-Apply: Changes are proposed via a pull/merge request. Scalr can automatically run a
planand report the output. After review and merge into the main branch, Scalr proceeds with theapplyoperation. This model ensures that only approved code is applied to the infrastructure. - Apply-Before-Merge (or Plan-and-Apply on PR): This model allows teams to view the impact of changes and apply them from a feature branch or pull request before merging. This can be utilized for iteration in development environments or for validating changes prior to mainline integration. This is similar to the Atlantis workflow.
Scalr's CI/CD automates standard Terraform/OpenTofu commands (init, plan, apply), reducing manual intervention and potential errors.
Custom Hooks for Workflow Extension
Standard IaC workflows may require steps beyond automated plans and applies. Scalr's custom hooks allow the integration of custom scripts and tools at various stages of a run lifecycle. These hooks enable customization of the CI/CD process.
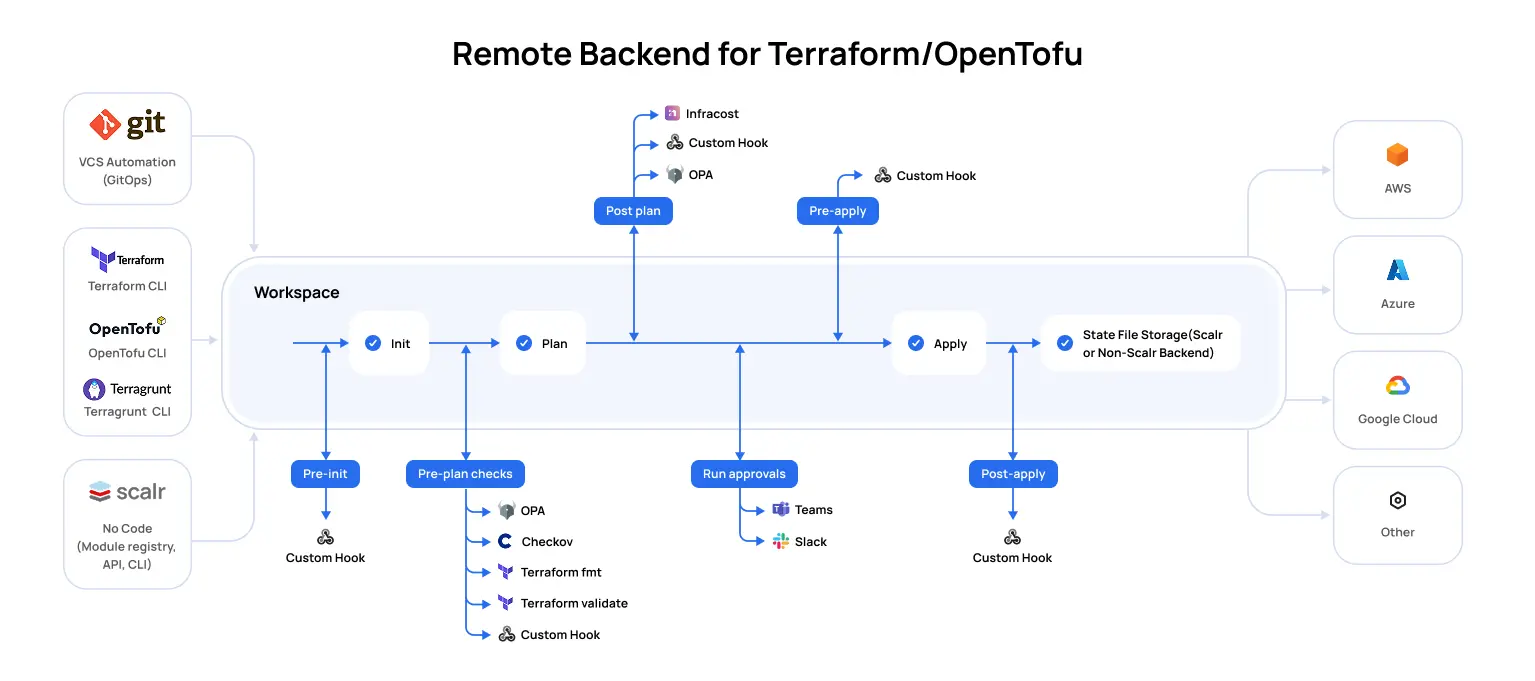
Available hook points include:
- Pre-init: Execute scripts before Terraform/OpenTofu initializes the backend and providers. This can be used for setting up dynamic configurations or fetching credentials.
- Pre-plan: Run scripts before the
planoperation. Used for static code analysis (e.g.,tfsec,tflint), compliance checks, or generating dynamic input variables. - Post-plan: Execute scripts after a
planhas been generated. This can be used for custom plan analysis, cost estimation checks, or sending notifications about planned changes. - Pre-apply: Run scripts before the
applyoperation. Used for final validation, integration with external approval systems, or security checks. - Post-apply: Execute scripts after changes have been applied. Used for sending deployment notifications, updating CMDBs, running integration tests, or cleaning up temporary resources.
Scripts for custom hooks can be sourced from a VCS repository or downloaded from an external location.
Hooks Registry
Scalr also supports a "hooks registry" for centralized management of hooks. This enables platform teams to define and maintain standard hooks for use by development teams, which can aid in consistency and adherence to best practices. Rather than applying the hook per workspace, it can be assigned to environments, and all workspaces in the environment will inherit it.
Webhooks
Webhooks provide the flexibility to integrate with any external system that can receive an HTTP POST request. This opens up possibilities for custom notifications, reporting, and integration with other automation tools.
To configure a webhook, you need to specify:
- Event: The Scalr event that will trigger the webhook (e.g.,
run:completed,run:errored). - URL: The endpoint of your external service that will receive the webhook payload.
- Secret Key: An optional key to verify the authenticity of the webhook payload.
For instance, you could configure a webhook to:
- Create a ticket in Jira or ServiceNow when a run fails.
- Trigger a custom script to perform post-provisioning configuration
Run Triggers for Dependency Management
Infrastructure components often have dependencies requiring coordinated provisioning and updates. Scalr's run triggers manage these dependencies.
Run Triggers offer the following capabilities:
- Chaining Workspace Runs: A workspace run can be configured to automatically trigger a run in another workspace upon successful completion, creating deployment pipelines (e.g., a network infrastructure update triggering an application deployment).
- Creating Dependencies Between Workspaces: Run triggers define explicit dependencies. If Workspace B depends on an output from Workspace A, a successful apply in Workspace A can trigger Workspace B to re-plan and apply, incorporating the latest outputs.
- Federated Environments: This feature allows the creation of dependencies between workspaces in different Scalr environments. This is applicable for scenarios such as promoting infrastructure changes between staging and production environments, or when different teams manage interconnected components in separate environments.
- VCS Event-Based Triggers: Run triggers can be initiated based on VCS events, such as a push to a specific branch or the creation of a tag. This integrates IaC automation with Git workflows.
Scalr's cross-workspace run triggering is comparable to features in other platforms like Terraform Cloud (TFC) or Spacelift for managing infrastructure dependencies.
Event-Driven Workflows
While webhooks and run triggers form the foundation, Scalr's native integrations are what elevate automation to build event-driven workflows. By connecting to services like AWS EventBridge, Datadog, Slack, and Teams, you can build intelligent systems that remediate issues, provide deep observability, and enable real-time collaboration.
AWS EventBridge
Use the AWS EventBridge integration to trigger automated remediation and orchestrate complex, multi-step workflows in response to Scalr events.
- Automated Rollbacks: A
run:erroredevent from a production Scalr workspace can be filtered by an EventBridge rule. This rule then invokes an AWS Lambda function that uses the Scalr API to queue a new run based on the last known-good commit, effectively initiating an automatic rollback without manual intervention. - Complex Deployment Orchestration: A successful
run:completedevent does not have to be the end of a workflow. Use it as a trigger in EventBridge to start an AWS Step Functions state machine. This allows you to orchestrate post-provisioning tasks, such as running a database migration, deploying application code via a different tool, and then invoking a Lambda function to perform smoke tests against the new environment. - Enforce Compliance: When a
workspace:createdevent occurs, EventBridge can trigger a Lambda function to inspect the new workspace's configuration. The function can verify that required security policies are enabled and that it is properly connected to version control, flagging non-compliant workspaces automatically.
Datadog
Integrating Scalr with Datadog allows you to directly correlate infrastructure changes with application behavior and monitor the health of your Terraform pipeline.
- Pinpoint Failure Causes: When a Scalr run completes, the event is sent to Datadog and overlaid as a marker on your APM and infrastructure graphs. If you see a spike in application errors or server latency, you can immediately identify if a specific infrastructure deployment was the cause, reducing time spent on root cause analysis.
- Monitor IaC Health: Treat your infrastructure pipeline as a production service. Create dashboards in Datadog to track key Scalr metrics like
run.durationto spot slow-downs, the ratio of successful to failed runs to measure reliability, and activity levels per workspace to understand usage patterns. Set up alerts for anomalies, such as a sudden increase in run failures for a critical environment. - Audit Security Changes: Send events from security-sensitive workspaces (e.g., those managing firewalls or IAM policies) to Datadog. Create monitors that trigger high-priority alerts whenever a change is applied in these environments, providing a real-time audit trail for your security team.
Slack & Teams
The integrations for Teams and Slack are used to deliver context-aware notifications that embed directly into your team's workflow, improving visibility and collaboration.
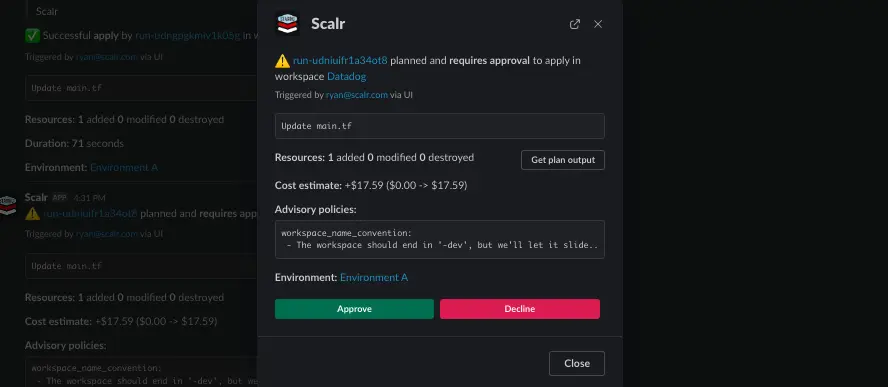
- Targeted, High-Signal Alerts: Instead of sending all notifications to one place, you can route them based on context.
run:erroredevents from production can post to an SRE on-call channel, whilerun:needs_actionevents can be sent to a development team lead channel to prompt an approval. This ensures the right people see the right information without creating unnecessary noise. - Streamline Code Reviews: When a developer opens a pull request, Scalr can run a speculative plan and post the results directly into the PR conversation thread in Slack or Teams. This allows reviewers to see the potential impact of an infrastructure change immediately, without leaving their chat client.
- Provide Stakeholder Visibility: For less technical stakeholders, you can direct
run:completedevents for major milestones—like a deployment to a staging environment—to a public project channel. This keeps product managers and other stakeholders informed of progress without them needing to ask engineers for status updates.
Customizable Execution Environments: Self-Hosted Agents
Execution environment requirements can vary. Scalr supports both managed execution on scalr.io runners and self-hosted agents (runners).
Self-hosted agents provide the following benefits:
- Network Access: Agents can be deployed within a private network, enabling access to non-publicly exposed resources like internal artifact repositories, secret management systems, or private cloud APIs.
- Custom Execution Environment: Users have full control over the agent's environment. This allows for the installation of extra tooling, binaries, or other CLI tools and dependencies required by custom hooks or IaC modules. The agent's operating system can be customized, allowing users to define their own execution image.
- Compliance and Security: For organizations with specific security or compliance requirements, self-hosted agents ensure that code and credentials remain within the controlled network perimeter during execution.
This customization allows Scalr to meet diverse organizational requirements.
Conclusion
Scalr is a platform for automating and governing Terraform and OpenTofu workflows. Its CI/CD capabilities, including GitOps support, custom hooks, run triggers, and customizable execution environments, assist teams in managing infrastructure. Scalr provides tools for various levels of IaC automation and deployment complexity.
Further information is available in the Scalr documentation. A demo can be requested to view these features.

